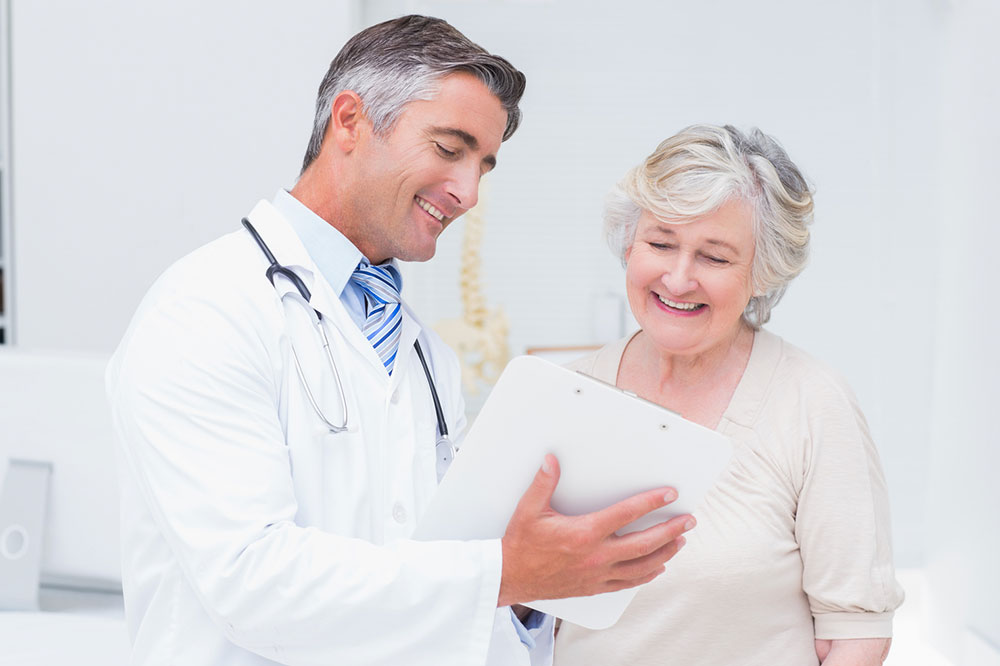
Kidney Disease Types, Signs, and Management
Kidney disease is a severe health condition that can lead to kidney failure. The organ helps to refine and remove waste products from the blood. When kidney disease occurs, it can damage different organs of the body and lead to serious health problems. This condition causes toxins to accumulate in the blood, causing kidney damage and impairing their function, which can be fatal if not treated promptly.
What are the causes of kidney disease?
High blood pressure
Elevated blood pressure can damage the kidneys over time by causing them to lose their ability to filter toxins and fluids from the bloodstream properly.
Diabetes
Diabetes increases your risk for kidney disease because it damages the blood vessels in your body, including those that supply blood to the kidneys.
Pyelonephritis (a type of urinary tract infection)
This can cause inflammation and scarring in the renal tissue, leading to kidney failure.
Vesicoureteral reflux
This is when urine backs up into the ureters, the tubes that carry urine from the bladder to the outside world. It often leads to renal failure if it’s not treated on time.
Interstitial nephritis
This is an inflammation of the kidney cells that results in decreased function or even loss of kidney function over time. It can be caused by various factors, such as infection with bacteria or viruses, exposure to toxins or chemicals, and autoimmune diseases like lupus.
Glomerulonephritis
It is an inflammation of the glomeruli (small cells in the renal pelvis that filter waste from the blood). It can be caused by infection, injury, or autoimmune diseases (such as lupus), and it often progresses slowly over time.
Autoimmune diseases
These involve your immune system attacking your body tissues (including your kidneys). This damage can lead to a gradual decline in kidney function over time, even without apparent symptoms.