Atopic dermatitis in infants – Early signs, causes, and management
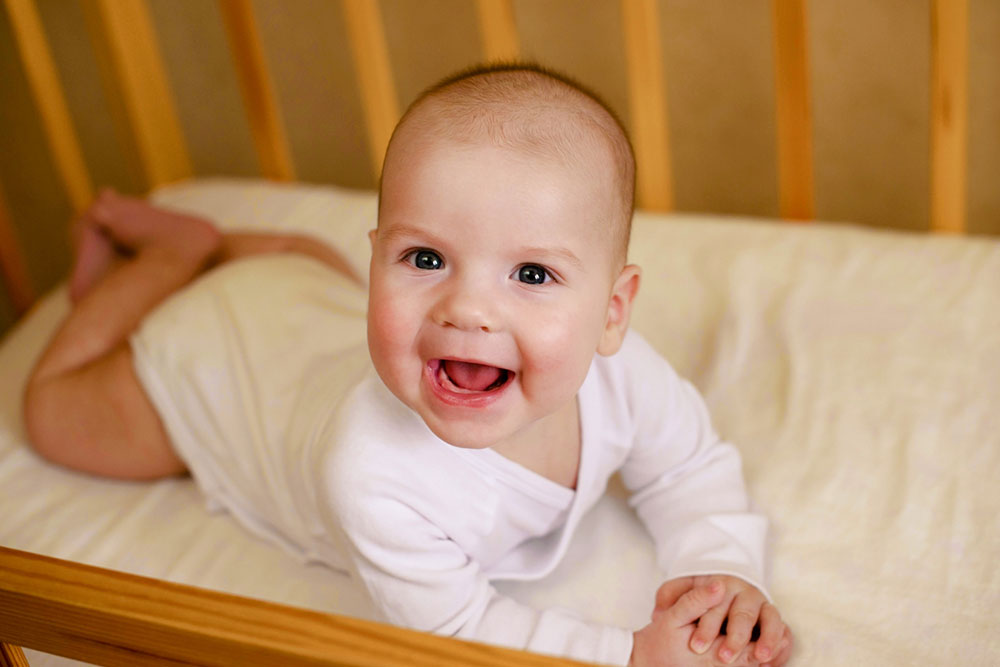
Atopic dermatitis or eczema is a chronic skin condition characterized by skin inflammation and irritation. Itchiness is a prominent and distressing symptom of the condition. The itch can be intense and lead to scratching, which can irritate the skin and cause it to thicken and develop small bumps. The condition can affect children and adults of all ages with flare-ups that may get out of control without prior warning. Here is a comprehensive overview of the condition.
Early signs of atopic dermatitis in infants
Itchy skin
One of the most evident signs of atopic dermatitis is intense itching on the surface of the skin, which can be particularly distressing for infants who cannot express their discomfort verbally. Keep an eye out for the redness and inflammation that develops with this itching, causing small bumps to pop out as well. The skin in eczema-prone areas also becomes dry, thickened, and scaly, developing a rough texture with disease progression. There is no telling how bad the skin problems can get, as it all depends on the periods of worsening (flare-ups) affecting infants with varying intensity levels.
Common sites
In infants, atopic dermatitis typically starts on the face, especially on the cheeks and chin. Visible redness and swelling here indicate early inflammation that should not be ignored at this stage as it may also quickly spread to affect the scalp, forehead, and other parts of the body.
Causes and potential triggers
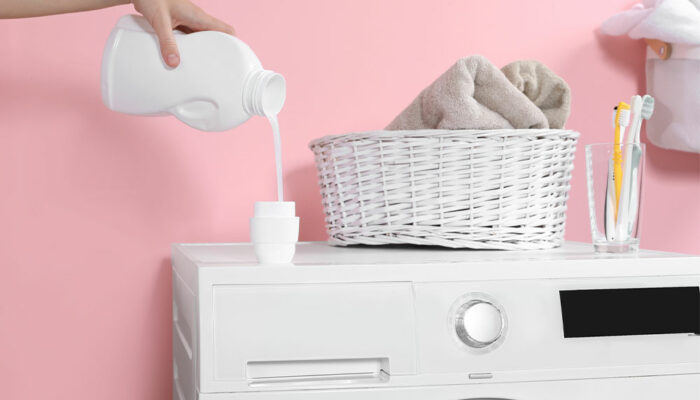
The precise cause of atopic dermatitis is not fully understood, but triggers and irritants often arise from a combination of genetic, immune system, and environmental factors. Potential external triggers for flare-ups also include allergens like pollen, dust mites, and pet dander found in the environment, skin irritants like harsh soaps and detergents, even weather changes and increased cortisol levels due to stress are potential triggers that one must pay attention to if early eczema among infants is suspected.