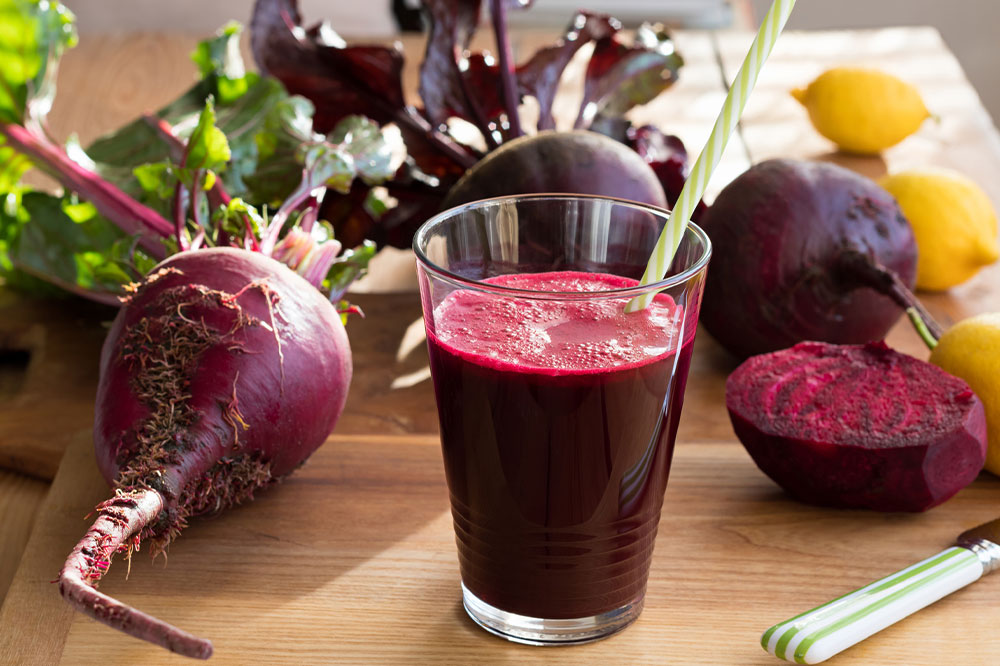
5 Best Foods for Managing Pulmonary Fibrosis
For individuals diagnosed with pulmonary fibrosis, managing their meal plans can be crucial in maintaining their overall health. The foods they consume can significantly impact their respiratory function and quality of life. Fruits, vegetables, and optimal hydration are necessary to keep pulmonary fibrosis in check. The right dietary choices can help reduce inflammation, improve lung function, and alleviate symptoms. Therefore, this article will explore foods that can help manage pulmonary fibrosis and maintain optimal health.
What is Pulmonary Fibrosis?
Pulmonary fibrosis is a lung disease that causes the development of fibrous, scar-like tissue in the lungs, making it harder for the lungs to work correctly. Over time, this scarring can become widespread, causing the lungs to lose their ability to expand and contract effectively, leading to reduced blood oxygenation.
Cystic fibrosis is a similar condition but develops in people since birth, thickening mucus in the lungs and making breathing difficult.
The most common symptoms of pulmonary fibrosis are:
- coughing
- shortness of breath
- fatigue
- chest pain
- a dry cough and
- losing weight unintentionally
The progression of the disease varies from person to person, and in some cases, the symptoms can develop rapidly, leading to acute respiratory distress (fluid build-up in the lungs).
Causes and treatments for Pulmonary Fibrosis
The causes of pulmonary fibrosis are not fully understood, but several factors have been identified as potential triggers. These include:
- exposure to environmental toxins such as silica and asbestos
- certain prescriptions
- autoimmune disorders
- genetics
While there is currently no permanent cure for pulmonary fibrosis, treatments are available to manage symptoms and slow down the progression of the disease. Moreover, cystic fibrosis medical treatment involves a range of interventions to manage symptoms and slow the condition’s progression.
These treatments include:
- Prescriptions such as immunosuppressants and antifibrotic drugs reduce lung inflammation and slow scarring.
- Oxygen therapy may also be necessary to improve breathing and reduce the risk of complications.